组会讲课人员:陈慧
Emerging Theranostic Nanomaterials in Diabetes and Its Complications
附加二茂铁的铱 (III) 二膦复合物可增强铁死亡的癌症免疫力
主讲人:陈慧
Sci Transl Med 2021, 13 (585) (IF 17.521) Pub Date: 2021-11-25 , DOI: 10.1002/advs.202102466
Abstract:
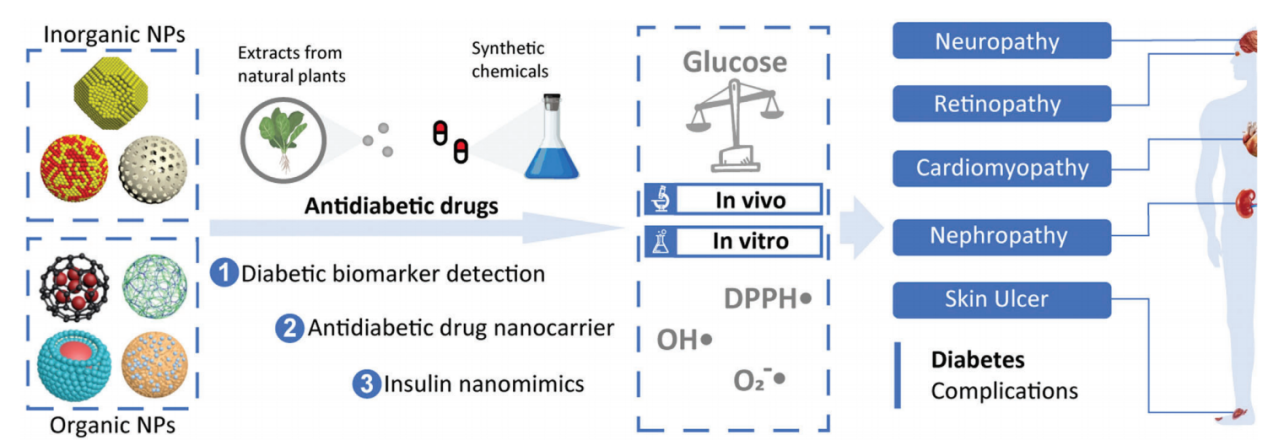
Diabetes mellitus (DM) refers to a group of metabolic disorders that are characterized by hyperglycemia. Oral subcutaneously administered antidiabetic drugs such as insulin, glipalamide, and metformin can temporarily balance blood sugar levels, however, long-term administration of these therapies is associated with undesirable side effects on the kidney and liver. In addition, due to overproduction of reactive oxygen species and hyperglycemia-induced macrovascular system damage, diabetics have an increased risk of complications. Fortunately, recent advances in nanomaterials have provided new opportunities for diabetes therapy and diagnosis. This review provides a panoramic overview of the current nanomaterials for the detection of diabetic biomarkers and diabetes treatment. Apart from diabetic sensing mechanisms and antidiabetic activities, the applications of these bioengineered nanoparticles for preventing several diabetic complications are elucidated. This review provides an overall perspective in this field, including current challenges and future trends, which may be helpful in informing the development of novel nanomaterials with new functions and properties for diabetes diagnosis and therapy.
摘要:
摘要:糖尿病是指一组以高血糖为特征的代谢紊乱。口服皮下注射的降糖药,如胰岛素、格列帕胺和二甲双胍可以暂时平衡血糖水平,然而,长期服用这些疗法会对肾脏和肝脏产生不良的副作用。此外,由于活性氧产生过多和高血糖诱导的大血管系统损伤,糖尿病患者有增加并发症的风险。幸运的是,纳米材料的最新进展为糖尿病的治疗和诊断提供了新的机会。本文综述了目前用于糖尿病生物标志物检测和糖尿病治疗的纳米材料的研究进展。除了糖尿病的传感机制和抗糖尿病活性外,这些生物工程纳米颗粒在预防糖尿病并发症方面的应用也得到了阐明。本文综述了该领域目前面临的挑战和未来的发展趋势,对具有新功能和新性能的新型纳米材料在糖尿病诊断和治疗中的发展具有一定的指导意义。