组会讲课人员:梁惠闲
Treatment of atherosclerosis by macrophagebiomimetic nanoparticles via targeted pharmacotherapy and sequestration of proinflammatory cytokines
巨噬细胞膜仿生纳米颗粒用于治疗动脉粥样硬化通过靶向药物治疗和促炎细胞因子隔离
主讲人:梁惠闲
Nature Communications (IF 15.805) Pub Date: 26 May 2020 DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16439-7.
Abstract:
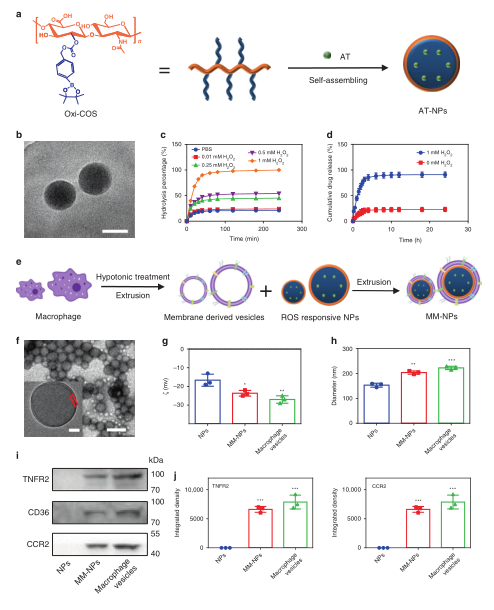
Vascular disease remains the leading cause of death and disability, the etiology of which often involves atherosclerosis. The current treatment of atherosclerosis by pharmacotherapy has limited therapeutic efficacy. Here we report a biomimetic drug delivery system derived from macrophage membrane coated ROS-responsive nanoparticles (NPs). The macrophage membrane not only avoids the clearance of NPs from the reticuloendothelial system, but also leads NPs to the inflammatory tissues, where the ROS-responsiveness of NPs enables specific payload release. Moreover, the macrophage membrane sequesters proinflammatory cytokines to suppress local inflammation. The synergistic effects of pharmacotherapy and inflammatory cytokines sequestration from such a biomimetic drug delivery system lead to improved therapeutic efficacy in atherosclerosis. Comparison to macrophage internalized with ROS-responsive NPs, as a live-cell based drug delivery system for treatment of atherosclerosis, suggests that cell membrane coated drug delivery approach is likely more suitable for dealing with an inflammatory disease than the live-cell approach.
摘要:
血管疾病仍然是死亡和残疾的主要原因,其病因通常涉及动脉粥样硬化。目前通过药物治疗动脉粥样硬化的疗效有限。在这里报道了一种源自巨噬细胞膜包被的ROS响应纳米颗粒(NP)的仿生药物递送系统。巨噬细胞膜不仅避免了NPs从网状内皮系统中的清除,还将NPs引导到炎症组织中,在炎症组织中NPs的ROS反应性能够实现特定的有效载荷释放。此外,巨噬细胞膜隔离促炎细胞因子以抑制局部炎症。药物治疗和炎症细胞因子从这种仿生药物递送系统中分离的协同效应导致动脉粥样硬化治疗效果的提高。与作为治疗动脉粥样硬化的基于活细胞的药物递送系统的ROS反应性NP内化的巨噬细胞相比,细胞膜包衣药物递送方法可能比活细胞方法更适合治疗炎症性疾病。