组会讲课人员:周艳虹
Treatment of atherosclerosis by macrophagebiomimetic nanoparticles via targeted pharmacotherapy and sequestration of proinflammatory cytokines
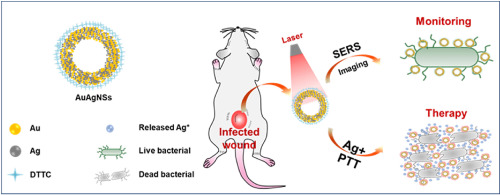
金银纳米壳促进耐药细菌感染的伤口愈合并通过表面增强拉曼散射成像进行监测
主讲人:周艳虹
Biomaterials. (IF15.304) 2020 Mar; 234:119763. DOI:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.119763.
Abstract:
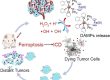
Chronic infections, caused by multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria, constitute a serious problem yet often underappreciated in clinical practice. The in situ monitoring of the bacteria-infected disease is also necessary to track and verify the therapeutic effect. Herein we present a facile approach to overcome the above challenges through a Raman tag 3,3′-diethylthiatricarbocyanine iodide (DTTC)-conjugated gold-silver nanoshells (AuAgNSs). With a strong responsive of the near-infrared laser due to surface plasmon resonance (SPR) from hybrid metallic nanoshell structure, AuAgNSs exhibits an efficient photothermal effect, and it simultaneously releases silver ions during laser irradiation to bacterial eradicate. Herein, two MDR bacteria strain, methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and extended-spectrum β-lactamase Escherichia coli, are chosen as models and studied both in vitro and in vivo. As a result, the AuAgNSs-DTTC substrates enable surface-enhanced Raman scattering imaging to provide a non-invasive and extremely high sensitive detection (down to 300 CFU mL−1 for MRSA) and prolonged tracking (at least 8 days) of residual bacteria. In a chronic MRSA-infected wound mouse model, the AuAgNSs gel-mediated photothermal therapy/silver-release leads to a synergistic would healing with negligible toxicity or collateral damage to vital organs. These results suggest that AuAgNSs-DTTC is a promising anti-bacterial tool for clinical translation.
摘要:
由多重耐药 (MDR) 细菌引起的慢性感染是一个严重的问题,但在临床实践中常常被低估。对细菌感染的疾病进行原位监测也是跟踪和验证治疗效果的必要条件。在此,我们提出了一种简便的方法,通过拉曼标记 3,3′-二乙基硫代碳菁碘化物(DTTC)-共轭金银纳米壳(AuAgNSs)来克服上述挑战。由于混合金属纳米壳结构的表面等离子体共振(SPR),AuAgNSs 对近红外激光有很强的响应,表现出高效的光热效应,并在激光照射过程中同时释放银离子以消灭细菌。在此,选择两种耐多药菌株,耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌(MRSA) 和超广谱 β-内酰胺酶大肠杆菌作为模型,并进行体外和体内研究。因此,AuAgNSs-DTTC 基板使表面增强拉曼散射成像能够提供非侵入性和极高灵敏度的检测(低至 300 CFU mL-1耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌)和残留细菌的长时间追踪(至少 8 天)。在慢性 MRSA 感染的伤口小鼠模型中,AuAgNSs 凝胶介导的光热疗法/银释放导致协同愈合,对重要器官的毒性或损伤可忽略不计。这些结果表明 AuAgNSs-DTTC 是一种很有前途的临床转化抗菌工具。